It's so incredible to harvest a garden full of vegetables that you grew yourself. When all the labor, planning, and caretaking pays off with abundant rewards, it's a beautiful day. But, now that it's all coming ripe at the same time, what do you do now? Thankfully, there are multiple ways to keep vegetables and fruits for months and years. Or, at least over the winter, so you'll always have fresh, fantastic vegetables at your fingertips.
Cold Storage
Root cellars, basements, spare rooms, and pantries have been used for cold storage for centuries. This method is best for root vegetables, like potatoes, yams, beets, turnips, carrots, sweet potatoes, onions, garlic, and winter squash and pumpkins. These vegetables keep for months without spoiling, as long as the temperature is between 32-45ºF. Also, the humidity is best between 80-90%. Cool climates reduce the growth of microorganisms, preserving the vegetables for long periods.
To utilize cold storage preservation in your home, simply find a room that meets the temperature and humidity requirements. Store the root vegetables in covered bins with dirt and straw. Arrange the winter squash and pumpkins singly, giving several inches of space between them for airflow.
Freezing
This method is the most time-effective. It's as simple as washing, cutting, and placing the fruit in a plastic bag, then in the freezer. Some vegetables need to be blanched before freezing, but even that is quick and easy. The downside to freezing is that if you lose power for an extended period, you could lose everything in it too. Having a back-up generator is necessary if you are using this as a primary method. Frozen foods, especially vegetables, often degrade in texture during freezing. Consult this guide to find the best candidates for long-term freezing.
Drying & Dehydrating
Dehydrating, or drying, the harvest is an excellent way to preserve on a large scale with minimal effort. To safely store vegetables and fruits this way, all the moisture needs to be removed. Moisture causes bacteria and mold to grow. One of the biggest benefits of this preservation method is that is doesn't require any special storage afterward. The dried foods are placed in tightly sealed glass or plastic containers, and that's it. Dehydrating is ideal for all vegetables, fruits, herbs, beans, and legumes. You can use a dehydrator, the oven, or the most simple, sun and air. This comprehensive drying guide covers all the options and techniques.
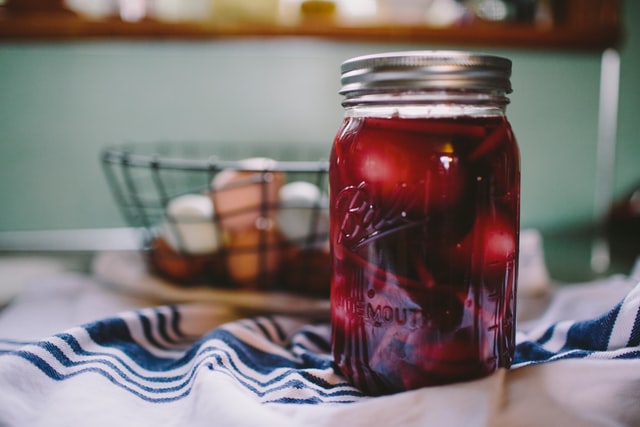
Canning
While canning isn't difficult, it is particular. Recipes must be followed precisely to ensure food safety during the process. Canning is appealing as a preservation method because it allows for longer storage of produce, and vegetables retain their quality better. Plus, making jams and jellies with excess fruit harvests is a fantastic way to preserve them. Water bath canning is the most straightforward technique, and the most common method for preserving vegetables, fruits, jams, sauces, and relishes.
Storing and preserving the garden harvest is necessary, so none of your hard work goes to waste. It's also important because it means home-grown, healthy vegetables are available to you and your family all year-round. Food security is a common worry too, and when you have your garden producing and your cellar filling up with preserved goodies, you can breathe easy.