Benefits of Rainwater Harvesting
- Cost Savings: One of the primary advantages of rainwater harvesting is the potential for significant cost savings on water bills. By using captured rainwater for non-potable purposes such as gardening and cleaning, you can reduce your reliance on municipal water supplies and lower your monthly expenses.
- Improved Plant Health: Rainwater is naturally free of the chemicals and additives found in tap water, making it better for the health of indoor and outdoor plants. The absence of chlorine and other disinfectants allows plants to thrive and grow more effectively.
- Reduced Flooding and Erosion: Rainwater harvesting helps to reduce the likelihood of flooding and erosion by mitigating water runoff. By collecting rainwater and directing it to storage tanks or into the ground, you can prevent excess water from overwhelming drainage systems and causing damage to your properties.
- Environmental Stewardship: By utilizing rainwater, you can contribute to the conservation of water resources and reduce your overall environmental impact. This practice helps to alleviate the strain on groundwater sources and eases the burden on municipal water supplies.
It is important to note that the regulations surrounding rainwater collection vary by state. Some states restrict water collection, while others have specific guidelines in place. Before embarking on a rainwater harvesting project, it is crucial to check the local regulations and obtain any necessary permits or permissions.
Types of Home Water Catchment Systems
There are several types of home water catchment systems available, ranging from simple DIY setups to more sophisticated commercial products. The choice of system will depend on factors such as cost, available space, and intended use of the captured water.
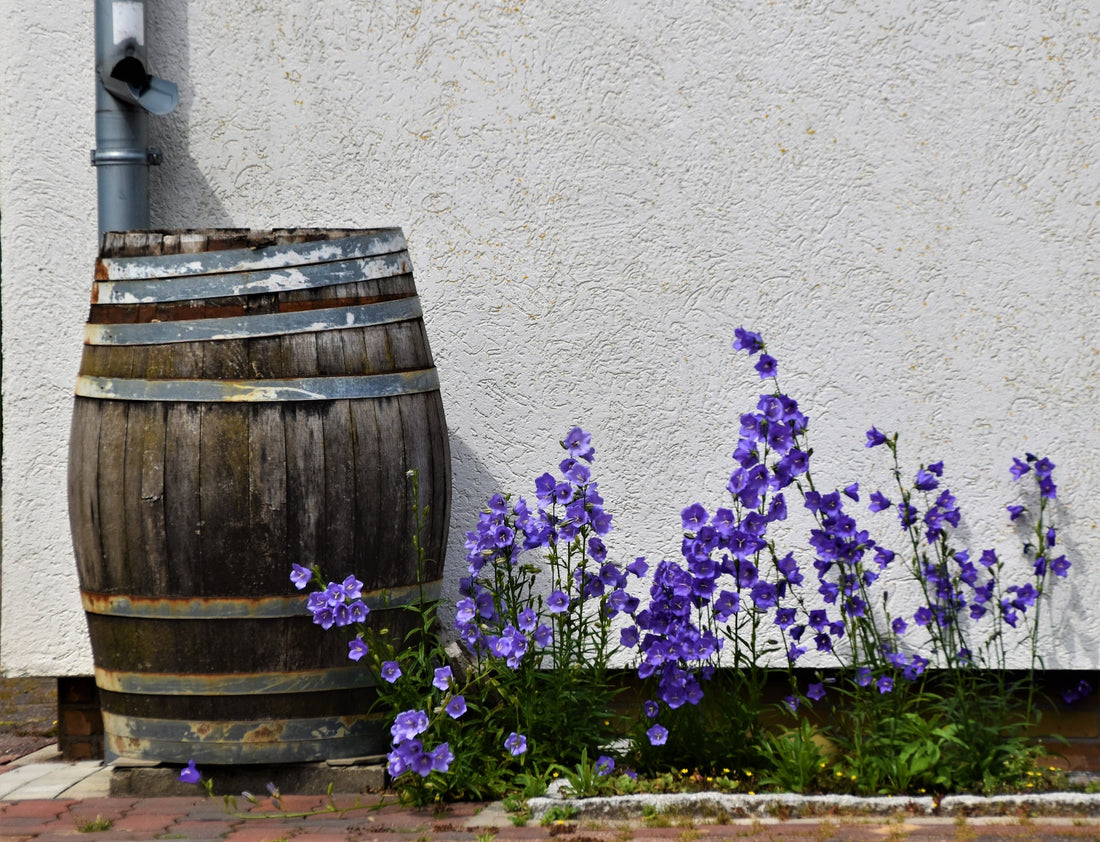
Rain Barrels
Rain barrels are a popular and affordable option for beginners looking to dip their toes into rainwater harvesting. These barrels, typically placed under downspouts, collect rainwater from rooftops. The captured water can then be used for various non-potable purposes, such as watering plants and cleaning.
To set up a rain barrel system, position the barrel under a downspout and ensure it has a screen to filter out debris and prevent mosquito breeding. Attach a spigot to the barrel for easy access to the collected water. The water can be used directly or connected to a hose for irrigation purposes.
Rain Gardens
Rain gardens are another effective way to utilize rainwater while enhancing the aesthetics of your landscape. These water retention zones are designed to capture and store rainwater, preventing runoff and allowing it to percolate slowly into the soil.
Cisterns
For those seeking a larger storage capacity, cisterns are an excellent option. These tanks can hold a significant amount of rainwater and are suitable for more substantial water needs, such as irrigation or non-potable household use.
Cisterns come in various sizes and can be above-ground, below-ground, or partially submerged. They should be made of non-reactive materials, such as reinforced concrete, galvanized steel, or plastic, to ensure water safety. It is crucial to implement proper pre-filtration systems to remove debris and contaminants from the collected rainwater.
A Word of Caution: Water Quality
While rainwater is generally considered safe for non-potable uses, it is essential to be aware of potential contaminants and take necessary precautions. Factors such as the method of collection, storage conditions, and potential contact with pollutants can impact the quality of harvested rainwater.
Unless you are willing to invest in regular testing and treatment to ensure the safety of the water, it is advisable to limit the use of harvested rainwater to non-drinking purposes. Prioritize the health and safety of your household members by relying on treated municipal water or other safe drinking water sources.
Utilizing Captured Rainwater
Once you have set up your home water catchment system, you can make the most of the captured rainwater for various purposes. Here are a few common uses for harvested rainwater:
Irrigation
One of the most popular applications of captured rainwater is irrigation. Whether you have a small garden or a sprawling landscape, using rainwater for irrigation can help conserve water and promote healthier plant growth.
Depending on the setup of your water catchment system, you can use gravity or install a pump to feed the water to your garden. Consider the elevation difference between the water source and the garden to determine the water pressure. Keep in mind that friction in the pipes or hoses may reduce the water pressure.
Outdoor Cleaning
Captured rainwater is ideal for outdoor cleaning tasks such as washing vehicles, cleaning outdoor furniture, or rinsing off patio spaces. Utilizing rainwater for these activities reduces your reliance on tap water and helps conserve this valuable resource.
Non-Potable Household Use
Rainwater can also be used for non-potable household purposes such as flushing toilets, washing clothes, or cleaning floors. Check your local regulations regarding the use of rainwater in these applications and ensure that the water is appropriately filtered and treated to prevent any potential health risks.